Latest update: May 20, 2025
Broken links are hyperlinks that lead users to a non-existent or inaccessible page, resulting in the infamous 404 error. These links can significantly degrade your website’s user experience and SEO performance, making it crucial to address them promptly.
What Are Broken Links?
Broken links, often recognized as dead links, are hyperlinks on a website that no longer function due to one or several reasons: the destination website has been removed, the page it’s pointing to has been relocated without proper redirection, or the URL structure of the linked site has changed without update. Encountering a broken link typically results in a 404 error page, signaling to the user and search engines that the content they’re attempting to access is not available. Not only do broken links disrupt the user experience, leading to frustration and reduced site credibility, but they also negatively impact a website’s SEO performance. Search engines, like Google, interpret broken links as signs of a neglected site, which can detrimentally affect the site’s ranking in search engine results pages (SERPs).
Why Are Links Broken?
Broken links occur when a webpage is moved or deleted without updating the hyperlink that points to it, leading to a dead end for users and search engines. Several factors contribute to broken links:
- URL Changes: If a webpage’s URL is altered (e.g., for SEO optimization) and the internal links pointing to that page aren’t updated accordingly, those links become broken;
- Website Restructuring: During a website redesign or restructuring, pages might be moved to different directories or removed altogether, causing links that point to those pages to break;
- Domain Migration: Moving to a new domain without properly redirecting the old URLs can result in numerous broken links;
- External Links: When linking to content on other websites, those URLs may change or become unavailable over time, leading to broken external links;
- Typos in URLs: Simple human errors, like typos when creating links, can also lead to broken links.
Why Are Broken Links Bad?
Broken links negatively impact user experience and website health in several ways:
- User Experience: Users encounter frustration and disappointment when they click on a link expecting relevant content but are met with a 404 error page instead. This can decrease user trust and increase bounce rates;
- Website Credibility: A high number of broken links can make a website appear neglected or outdated, damaging its credibility and professionalism;
- SEO Impact: Search engines like Google use links to discover and index content. Broken links halt this process, potentially limiting a website’s visibility in search results. Moreover, they waste crawl budget, which is the limited time or number of pages a search engine allocates to crawl a website;
- Link Equity Loss: For SEO, links pass value and authority from one page to another. Broken links disrupt this flow, leading to a loss of link equity and potentially affecting page rankings.
How to Find Broken Links?
Identifying broken links is a crucial step in maintaining a website’s health and user experience. Here’s how you can find them:
- Google Analytics: Use Google Analytics to track 404 errors by setting up a custom report. Filter page views by your 404 page title (often includes “Page Not Found” or a similar phrase) to identify URLs that lead to broken links;
- Google Search Console: The Coverage report in Google Search Console highlights pages with errors, including 404s. This tool is instrumental in finding broken internal and external links, providing insights into how these issues affect your site’s indexing;
- Dedicated SEO Tools: Utilize SEO tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, and Moz.These platforms offer site audit features that crawl your website to detect broken internal and external links, providing reports and actionable insights;
- Manual Checking: For smaller websites, manually clicking through each link can be feasible. This method, while time-consuming, ensures you understand the user journey on your website.
How to Find Broken Links with Google Analytics?
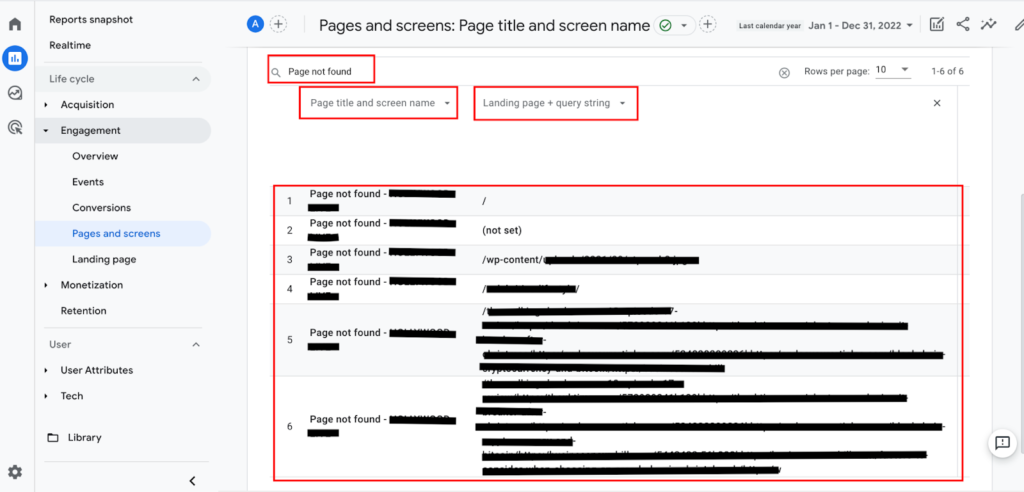
To identify broken links using Google Analytics, you need to track 404 errors, which indicate a broken link when a user lands on a non-existent page. Here’s a detailed approach:
Create a Custom Report
- Navigate to your Google Analytics account;
- Go to “Customization” > “Custom Reports” > “+ New Custom Report”;
- Title your report (e.g., “404 Errors”);
- For the report type, choose “Flat Table”;
- Set “Page Title” and “Page” as dimensions;
- Choose “Unique Pageviews” as the metric;
- Apply a filter where “Page Title” contains the title of your 404 page (e.g., “Page Not Found”);
Analyze the Report
- Access the report you created under the “Custom Reports” sectio;
- This report shows you the URLs that users attempted to visit but resulted in a 404 error, indicating a broken link.
Identify Referral Paths
To find out how users are reaching these 404 pages, add a secondary dimension called “Full Referrer” to see the source URL.
This process helps in pinpointing exactly which broken links need attention and where they’re being linked from.
How to Fix Broken Links in WordPress?
WordPress simplifies the process of fixing broken links with plugins and manual methods:
Using a Plugin
- Install a plugin like “Broken Link Checker“;
- Once activated, it automatically scans your site for broken links;
- Navigate to the plugin’s settings to view a list of broken links;
- You can edit or unlink each broken link directly from the plugin’s interface.
Manual Fix
- If you know the broken link URL, go to “Posts” or “Pages” in your WordPress dashboard;
- Use the search function to find the content containing the broken link;
- Edit the content to correct or remove the broken link.
How to Check for Broken Links with Ahrefs?
Ahrefs offers a comprehensive toolset for identifying broken links both internally and externally:
Use Site Audit Feature
- Navigate to the “Site Audit” section and create a new project for your website;
- Once the audit is complete, go to the “Issues” tab;
- Look for issues labeled as “404 page” or “Broken links”;
Review Broken Links
- Ahrefs categorizes the broken links into internal and external;
- Each broken link issue provides detailed information, including the source page and the broken link URL.
Plan Your Fixes
- For internal broken links, update or remove the links from your site’s content;
- For external broken links, consider reaching out to the website owner to inform them of the issue or removing the link if it’s no longer relevant.
Using these methods, webmasters can maintain the health and usability of their websites, ensuring a positive user experience and aiding in SEO efforts.
How to Find Broken Links in Google Search Console?
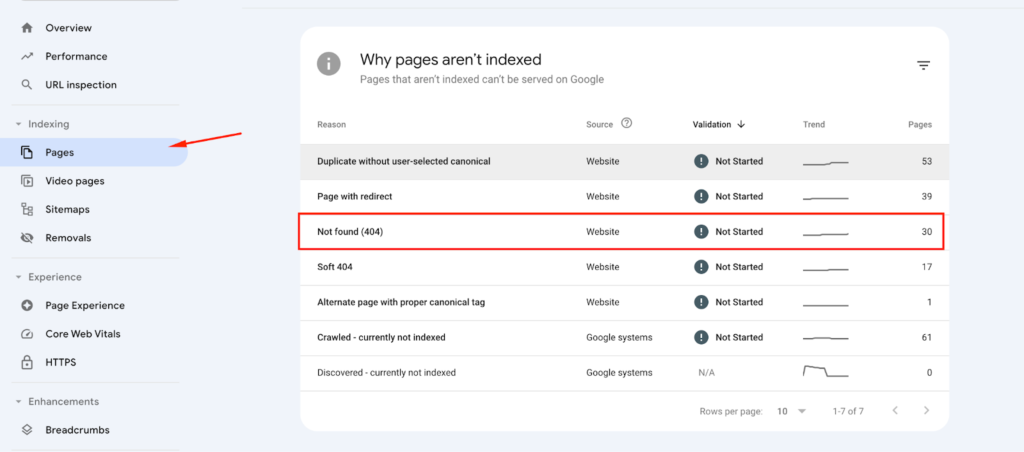
Google Search Console (GSC) is a powerful tool for monitoring your site’s performance in Google search results, including tracking broken links. Here’s how to use GSC to find broken links:
Navigate to Coverage Report
- Log into your Google Search Console account;
- Select the property (website) you want to inspect;
- Click on “Coverage” from the left-hand menu to access the report.
Identify Errors
- Within the Coverage report, look for the “Error” status. These errors often include Not Found (404) pages, which indicate broken links;
- Click on the “Error” tab to see a detailed list of URLs that Googlebot couldn’t crawl due to 404 errors.
Inspect and Export:
- You can click on each URL to see more details, including when Google last tried to crawl the page and where the broken link was found;
- Export this information for further analysis and tracking by clicking on the “Export” button.
Using GSC allows you to directly address the broken links Google is aware of, which can have a direct impact on your search engine optimization efforts.
How to Find Broken Links with SEMrush?
SEMrush offers comprehensive site audit features that help identify broken links among other issues. Here’s how to leverage SEMrush for this purpose:
Start a Site Audit
- Log into your SEMrush account and navigate to the “Site Audit” section;
- Create a new project for your website or select an existing project;
- Run the site audit to analyze your entire website.
Analyze Audit Results
- Once the audit is complete, go to the “Issues” tab;
- Look for issues categorized under “Notices” or “Errors” related to broken links, such as “Broken internal links” and “Broken external links.”
Review and Export Broken Links
- SEMrush provides a list of both internal and external broken links, including the page on which the broken link is located;
- Export the list to prioritize and track your progress as you fix these links.
SEMrush not only identifies broken links but also categorizes them, making it easier to prioritize fixes based on their potential impact on your site’s SEO.
How to Find Broken Links Moz?
Moz’s Site Crawl feature is instrumental in identifying and helping you delete or fix broken links. Here’s a streamlined approach using Moz:
Perform a Site Crawl
- Access your Moz account and select the “Site Crawl” feature within your dashboard;
- If you haven’t already, set up your site for Moz to crawl and analyze.
Identify Broken Links
- After the crawl is complete, Moz presents a report detailing various issues, including broken links categorized under “4xx errors”;
- These errors represent broken or dead links that return a 404 error status code.
Export and Address Issues
- Use Moz’s detailed reporting to review the broken links found on your site, including both internal and external ones;
- Export the report to systematically address these links, either by updating, removing, or replacing them on your site.
Moz helps streamline the process of identifying broken links, providing actionable insights to enhance your website’s health and user experience.
How to Fix Broken Links?
Once you’ve identified broken links on your website, the next step is to fix them to restore usability and SEO integrity. Here’s a process for fixing those links:
- Update the Link: If the broken link points to content that has moved, update the hyperlink to reflect the new URL. This is the most straightforward solution for internal links or external links with known new destinations;
- Remove the Link: If the content no longer exists and there’s no relevant replacement, consider removing the link altogether. This might be necessary for external links where the destination page is permanently removed;
- Use Redirects: Implement 301 redirects for moved content. This is especially useful for internal links if you’ve changed your website’s URL structure or migrated to a new domain. A 301 redirect signals to search engines that the page has moved permanently, transferring the link’s SEO value to the new URL;
- Replace the Link: For external broken links, find an alternative source that provides similar information and update the link accordingly. This ensures your content remains valuable and informative, despite the original source’s unavailability;
- Use a Broken Link Checker Plugin in WordPress: For websites built on WordPress, plugins like Broken Link Checker can automate the process of finding and fixing broken links. These tools scan your site regularly and allow you to update or unlink broken links directly from the plugin’s interface.
By actively finding and fixing broken links, you not only enhance your website’s user experience but also maintain its SEO health, ensuring your site remains accessible and valuable to both users and search engines.
Does Google Care About Broken Links?
Yes, Google cares about broken links for several reasons:
- Indexing and Crawling Efficiency: Broken links hinder Google’s ability to crawl and index a website efficiently. When Googlebot encounters a broken link, it hits a dead end, wasting the crawl budget allocated for the site and potentially missing out on indexing valuable content;
- Quality Signals: Google aims to provide users with the best possible search experience, which includes directing them to high-quality, relevant content. A website riddled with broken links sends a signal of poor maintenance and low quality, which Google may consider when determining search rankings;
- User Experience: Google’s algorithms are increasingly focused on user experience as a ranking factor. Broken links create a poor user experience, which Google aims to minimize in its search results. While a few broken links might not have a significant impact, a pattern of neglecting website health can affect a site’s overall ranking.
Google’s Webmaster Guidelines advocate for maintaining clean, well-structured websites that provide value to users. Regularly monitoring and fixing broken links is part of this upkeep, emphasizing the importance of addressing broken links to stay in Google’s good graces.
Conclusion
Broken links pose significant challenges to website usability and SEO performance, necessitating prompt attention from website owners. These links disrupt user experience, diminish site credibility, and negatively impact search engine rankings. Utilizing tools like Google Analytics, Google Search Console, SEMrush, Ahrefs, and Moz can help identify and address broken links efficiently. By promptly fixing broken links through updating, removing, or redirecting them, website owners can enhance user experience, maintain SEO integrity, and ensure their site remains accessible and valuable to both users and search engines. As Google prioritizes clean, well-maintained websites in its search results, addressing broken links aligns with best practices outlined in Google’s Webmaster Guidelines and contributes to overall SEO success.


