Latest update: May 20, 2025
Scraped content, a concern for many webmasters and SEO specialists, refers to the practice of taking content from other websites and publishing it on one’s own without adding value or originality. This guide delves into the nature of scraped content, its implications for SEO, Google’s stance on the issue, and strategies to protect your content from being scraped.
What is Scraped Content?
Scraped content involves taking material from other sources on the web and republishing it as if it were one’s own. It’s a violation of copyright laws and goes against the guidelines set by search engines, which demand originality and value in content.
How Is Content Scraped?
- Modifications by Scrapers: The second article emphasizes that content scrapers might use slight modifications, such as synonyms or automated generation techniques, to avoid detection. This is an addition to the broad description of scraping methods already mentioned;
- Types of Tools Used: It specifically highlights that besides manual methods, sophisticated bots are often used for scraping, which can gather data from websites rapidly.
Types of Content Scraped
This section was not covered in your original text. It details various kinds of content vulnerable to scraping, including:
- News articles, blog posts, multimedia content, technical publications, and more;
- Financial data, product catalogs, pricing information, and reviews.
The Detrimental Effects of Using Scraped Content
Using scraped content can lead to several problems:
- Penalties from Google: Websites with non-original content can be demoted in search rankings or removed from search results entirely;
- Legal Repercussions: Copyright infringement can lead to legal actions from the original content creators;
- Damage to Reputation: Audiences and partners may lose trust in a brand that fails to provide original content.
Google’s View on Scraped Content
Google explicitly discourages the use of scraped content. According to Google, websites should add value and present original content to their users. Google’s algorithms are designed to favor unique content and provide users with the best possible search experience, penalizing sites that rely heavily on content from other sources.
Preventing Content Scraping
Protecting your website from scrapers involves several technical and legal steps:
- Implement Technical Barriers: Use tools and methods like CAPTCHA, restricting API access, and monitoring unusual traffic patterns;
- Legal Measures: Copyright notices and legal actions against offenders can deter scraping activities.
Detecting Scraping Activities
Monitoring your web traffic for unusual patterns or spikes can indicate scraping in SEO attempts. Additionally, setting up Google Alerts for unique phrases from your content can help detect when your content is republished elsewhere without permission.
How to Prevent Content Scraping
- Limitation of Data Exposure: Limit the amount of accessible content through public APIs;
- Dynamic Content Delivery: Serve content dynamically to make it harder for SEO scrapers to extract useful data;
- Legal Warnings: Clearly state the legal consequences of content theft on your site.
Can Websites Detect Scraping?
Yes, websites can detect SEO scraping through various means, such as monitoring for suspiciously high traffic volumes from single IP addresses or unusual patterns of access that deviate from normal user behavior.
Google’s Guidelines on Scraped Content
Google urges webmasters to avoid creating sites with exclusively scraped auto content and encourages the addition of unique, valuable content. Sites found to be in violation may face removal from Google’s index, significantly impacting their visibility and traffic.
Content Scraping vs. Syndication
- Clarification of Terms: The article distinguishes between content scraping and syndication, explaining that syndication involves permission and proper attribution, whereas scraping does not;
- Guest Blogging: It mentions guest blogging as a form of syndication that can be beneficial for SEO if done correctly by linking back to the original content.
Legal Standing
Legality of Scraping Public Data: It notes a legal perspective that not all scraping is illegal. Data from publicly accessible sites without copyright can be scraped legally, but republishing that content without attribution constitutes plagiarism.
Why People May Allow Content Scraping
Some webmasters may tolerate content scraping if it results in backlinks to their original site. These backlinks could potentially be recognized as legitimate by search engines. However, it’s important to note that the quality of these links is typically not high. While they might not directly harm a website’s SEO, they don’t generally provide significant benefits either. This perspective suggests a more nuanced view of content scraping, recognizing that in some cases, it might passively aid in link building, even if the overall impact remains limited.
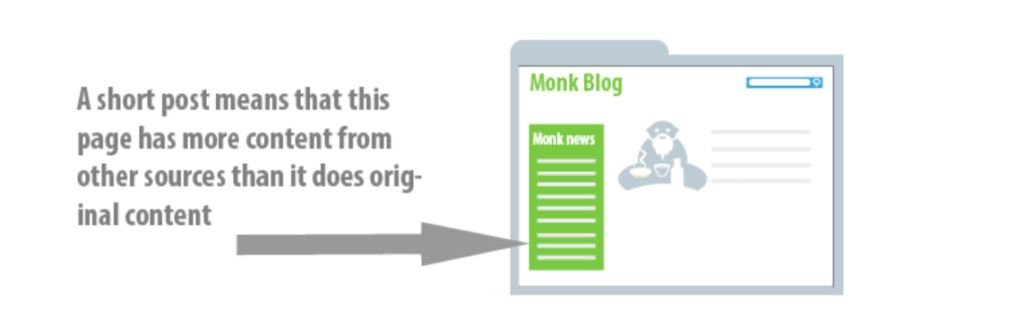
Balancing Scraped Content on Your Webpage
Google has not specified a precise limit, but a practical rule is that content sourced from other sites should ideally make up no more than 10 percent of your webpage’s content. Consider a typical blog with a news feed in the sidebar: if your blog post is brief, the news feed could inadvertently become the dominant content on the page.

In such cases, if the bulk of the page consists of scraped content, along with repetitive elements like logos and footers, search engines might view the page as lacking original content. This could lead to the webpage not being recognized as a valuable resource on the topic it purports to cover. Essentially, keeping external content to a minimum ensures that your site remains original and valuable to both users and search engines.
Conclusion
The integrity of your website’s content is pivotal for maintaining high SEO rankings and fostering trust with your audience. Abiding by Google’s guidelines against scraped content not only ensures compliance with legal standards but also upholds the quality and originality of your web presence. As the digital landscape evolves, prioritizing original content creation and implementing robust protection measures against scraping will safeguard your site’s reputation and scraper SEO performance.