Latest update: April 24, 2025
Crawling and indexing are extremely important for any site to rank. However, you might face different problems that can disrupt these processes, like the “Google Crawl Anomaly”.
This issue might lead to lower rankings and a drop in inbound traffic. So, ignoring crawl issues is not an option. We want to tell you how to diagnose and resolve it.
Keep reading!
What Is a “Google Crawl Anomaly”?
A “Google Crawl Anomaly” is an irregular issue Google faces. It appears in GSC when Google initiates a crawl of your page and experiences an unexpected problem.
This anomaly does not fit into predefined error classes, like:
- DNS problems;
- Server errors (5xx);
- 404 errors;
- Robots.txt blockages.
So, it won’t be that easy for you to pinpoint what provoked it.
The “Google Crawl Anomaly” might suggest momentary setbacks with the server or interruptions in the network. Even unexpected HTTP response codes that Googlebot cannot interpret might cause it.
How can this issue impact your site operations?
Delayed Indexing
This error is preventing Googlebot from reaching important pages on your site. So it won’t index or upgrade them in search results. This may affect engagement and relevance as people will see outdated content more often.
Lower Crawl Budget
Google gives a limited number of crawl requests to each site. Persistent anomalies may push Google to deprioritize crawling your pages. So, it will take you way more time to bring your updates to the top.
Negative Ranking Impact
Search engines prefer accessible and well-structured sites. Frequent crawl anomalies may act as a signal of poor site health. As a result, you will notice a drop in rankings.
Loss of Traffic
If your key pages are unreachable, they may not appear in the listing. You’ll ultimately see a drop in organic traffic, which is particularly risky when you’re reliant on visibility for revenue.
Poor User Experience
Crawl abnormalities might indicate deeper technical issues that could influence UX, including
- Slow load times;
- Broken links;
- Improper redirects.
Common Causes of the “Google Crawl Anomaly”
As you already know, the “Google Crawl Anomaly” arises when Googlebot faces challenges while attempting to crawl your resource. Your site doesn’t get proper indexing, and your visibility becomes lower.
You need to understand what might generate this issue. So, we gathered the common causes below.
Server Problems
If a server goes down, even temporarily, Googlebot may fail to access your site.
High server loads can lead to slow response times or even timeouts that also stop crawling. Some of the activities that might lead to an overload are
- Excessive user traffic;
- Bot activity;
- Bad resource optimization.
Server misconfigurations, like incorrect HTTP headers or faulty caching rules, may inadvertently block Googlebot as well. The bot won’t analyze the current condition of your resource if the server returns inconsistent HTTP status codes.
Blocked Resources
Googlebot depends on different resources when it comes to rendering your pages. So, CSS or JavaScript restrictions may cause a “Google Crawl Anomaly”, as the bot can’t fully understand and index your content.
Also, firewalls might sometimes mistake the crawler for a threat and block its requests.
Plus, you might unintentionally add the bot to your user-agent blocklist, which leads to indexing difficulties.
Internal Links and Redirects
URL issues may also complicate work for Googlebot and interrupt the crawling progress.
For example, broken links lead to lost pages that return 404s. They don’t allow the bot to index your resources.
Incorrect redirect configurations may also cause a “Google Crawl Anomaly”. The crawler can’t get to the last endpoint when it experiences redirect loops or excessive chains.
DNS Errors
Problems with DNS might also cause this error.
For instance, Googlebot will struggle to establish a connection if your DNS server is experiencing high latency. Propagation delays can also lead to crawl failures.
Plus, an inappropriate configuration of DNS records often misdirects the bot to locations that don’t exist or aren’t intended.
Step-by-Step Guide to Fixing the “Google Crawl Anomaly”
The “Google Crawl Anomaly” can be really frustrating. It doesn’t always have a clear cause, which complicates troubleshooting for you. You need to follow a structured plan to investigate and settle this problem efficiently.
Step 1: Locate Affected Pages
Log in to your Google Search Console and open the Pages section. It will give you an overview of your indexed and non-indexed pages.
Find the “Crawl Anomaly” alert and click on it to examine all the details.
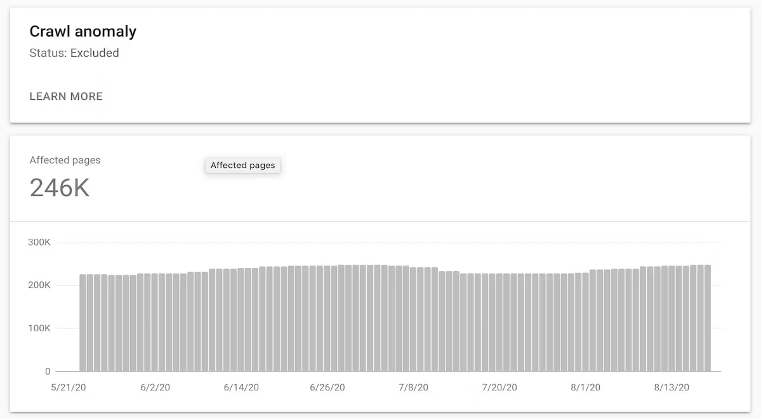
You will see the date of the last crawl attempt. Plus, the report will include any additional error messages that might hint at the origin of the problem.
Step 2: Test the URL
After you determine the problematic pages, use the URL Inspection Tool to test them. Enter the link into the tool to check its live status by selecting Test Live URL.
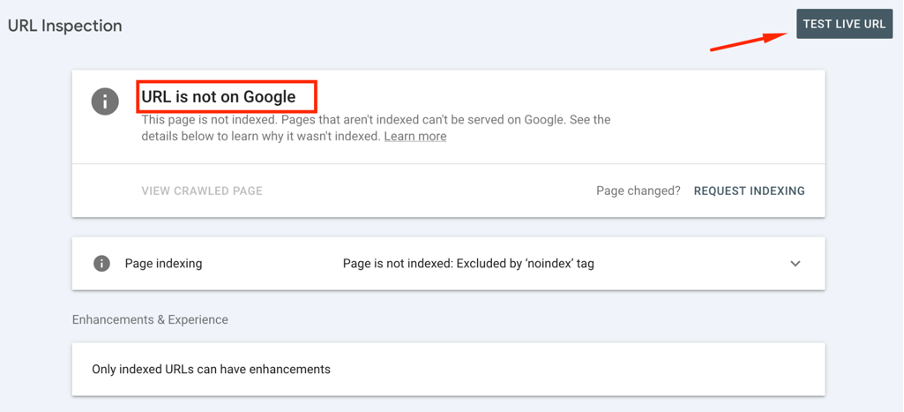
It will help you reveal any specific issues, like:
- 403;
- 404;
- 500;
- DNS problems, etc.
Plus, you might run your URL through the Lighthouse tool. It lets you confirm that Googlebot doesn’t experience rendering difficulties on mobile devices.
Step 3: Inspect Your Server
You already know that the “Google Crawl Anomaly” might appear because of server-related issues. So, you need to verify that your site’s server is running smoothly.
First, access your server logs to check if it’s processing the crawl requests correctly.
Make sure to review the following aspects to confirm they’re not blocking Googlebot:
- Rate limiting;
- Firewall settings;
- Security settings;
- DNS modifications.
Step 4: Inspect Robots.txt and Meta Tags
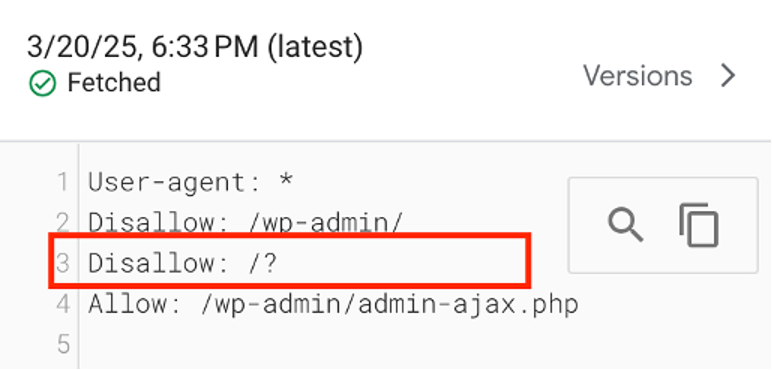
Your robots.txt file plays a huge role in directing crawlers. Open this file and examine its directives to confirm it’s not blocking Googlebot.
Look for any restrictive rules, like
- Disallow: /;
- User-agent: Googlebot.
Plus, you need to check if your pages don’t have the “noindex” tag. Make adjustments if necessary and test the changes with Google’s robots.txt Tester tool.
Step 5: Fix Internal and External Linking Problems
Internal and external links also help browsers navigate your site. We’ve mentioned before that broken or wrong links lead to the “Google Crawl Anomaly”.
So, audit the involved pages to verify that all links are accurate and functional.
Plus, we recommend you inspect canonical tags to confirm that they are pointing to the intended version of the page. Otherwise, Google may struggle to index it properly.
Step 6: Monitor and Request Reindexing
Go back to the Google Search Console after applying all necessary fixes. Open the URL Inspection Tool we mentioned above to check the updated status of your page. Click on the “Request Indexing” button in the right corner.
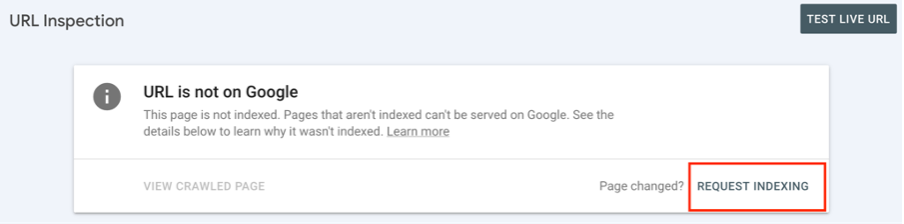
Googlebot will visit your page again and inspect the modifications you made. We advise you to monitor the Indexing Report over the next few days to confirm the problem is gone.
How to Prevent Future Crawl Anomalies
Google crawl anomalies disrupt indexing and impact your site’s visibility. You already know how to fix these issues. Now, we want to offer you some extra tips on how to control them in the future.
Try to regularly check your GSC stats and reports for errors and blocked resources.
Make sure to optimize your site and create a logical linking structure. Complete the following steps:
- Use a clear hierarchy;
- Minimize orphan pages;
- Put all important pages in the main navigation;
- Use meta tags smartly.
Also, use 301 redirects for permanent changes and minimize redirect chains to ensure efficient crawling. Resolve any duplicate content concerns and update your XML sitemap from time to time.
Remember that search engines update their algorithms and crawling behavior regularly. So, read the official documentation and adapt your strategy accordingly.
Key Takeaways in Fixing the “Google Crawl Anomaly”
- The “Google Crawl Anomaly” can be very confusing as it usually doesn’t have an obvious cause. Still, it leads to indexing problems and a drop in traffic;
- Possible causes include server problems, blocked resources, and DNS issues;
- To fix the error:
- Locate affected pages.
- Check for server problems.
- Update blocked resources.
- Fix any issues with links.
- Keep your site structure logical and clear.
Make sure to visit your GSC periodically to catch any crawl anomalies right away.
If you encounter other errors, refer to our Google Search Console guidelines to resolve them.


