Latest update: April 16, 2025
If you’ve spotted “Not Found (404)” errors in Google Search Console, it means Google tried to crawl a URL on your site but couldn’t find the page.
These errors can be caused by broken links, incorrect URLs, or missing redirects—and frequent 404s can hurt both user experience and search rankings.
In this guide, we’ll explain what causes “Not Found (404)” errors and how to fix them.
What Does a “Not Found (404)” Error Mean?

A “Not Found (404)” error is among the most typical issues you might have with your site. It is an HTTP status code response. It shows that the server couldn’t locate the requested resource.
This error appears when the system is reachable, but it can’t track down the exact URLs. It often implies that the page was deleted or moved.
Visitors see a default browser notification or an individualized error page when experiencing 404s.
The error itself doesn’t reflect a network downtime. Still, it might undermine user satisfaction and your reputation.
Main Causes of the Not Found (404)
Here are some of the main causes of this error.
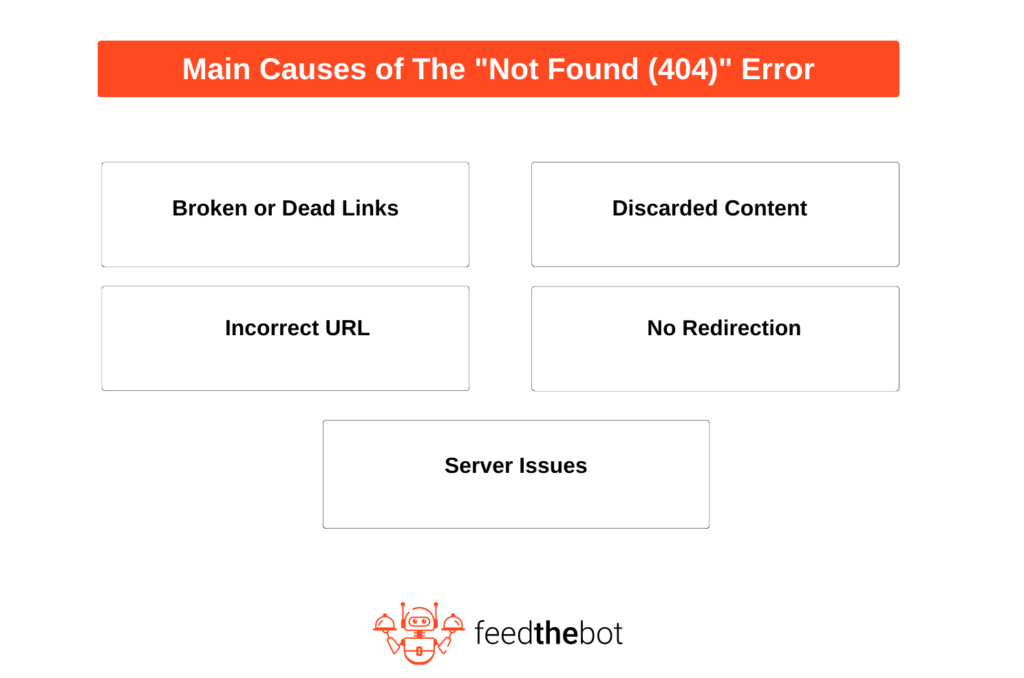
Broken or Dead Links
Users may face this error if they follow old links from other websites or bookmarks. They receive this status code if you discard your content without appropriate redirection.
These broken links pile up over time and make the navigation problematic for your visitors.
Incorrect URL
An incorrect URL often leads to the “Not Found (404)” error. The system can’t find the requested page if people do the following actions:
- Mistype a domain name;
- Include extra characters;
- Format the URL wrongly.
Discarded Content
If you remove a resource and don’t offer a substitute, your visitors will receive a 404 error when accessing the content. It’s pretty common for:
- Outdated articles;
- Expired products;
- Discontinued services.
No Redirection
Sometimes, you may need to restructure your site or move pages to new URLs. You’ll have to use 301 or 302 redirects for that purpose. Otherwise, people who attempt to reach the expired URL will face a 404 error rather than getting to the new location.
Server Issues
Server configuration mistakes or difficulties with CMS may lead to 404 errors as well. People can’t get the files and pages they need if the server fails to keep or index them.
Step-by-Step Guide to Fixing the “Not Found (404)” Error
If “Not Found (404)” error happens too often, this error might negatively influence user experience and indexability.
So, we want to tell you how to manage the unexpected 404s. Follow the steps we outlined.
Step 1: Check Not Found (404) Report
First, you have to open your Google Search Console. Go to the “Pages” area beneath “Indexing.” You will see a list of URLs that Google marked as a “Not Found (404)” error in this section.
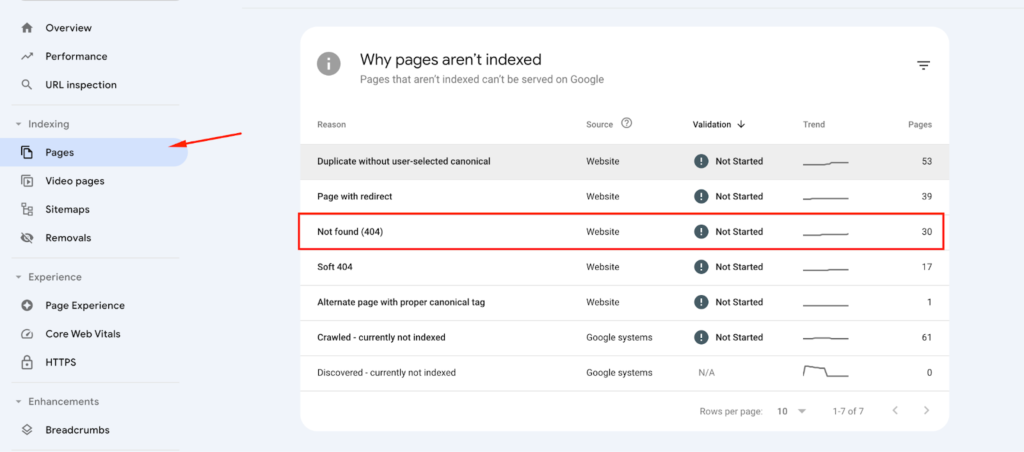
Next, you have to export the list so you can analyze the links more effectively. Evaluate the cause of each error and determine which URLs demand your attention.
Step 2: Apply Corrective Actions
After you determine what caused each 404 error, you have to take some corrective actions.
Recover Removed or Relocated Content
First, check if some of your pages were deleted unintentionally. If that’s the case, consider restoring them.
If you moved the content, make sure people can still access it through updated navigation menus or proper redirects.
Plus, it is advisable to inspect your CMS or file manager to prove the condition of the nonexistent page.
Use 301 Redirects
Use 301 redirect to forward users and Googlebot to a new URL.
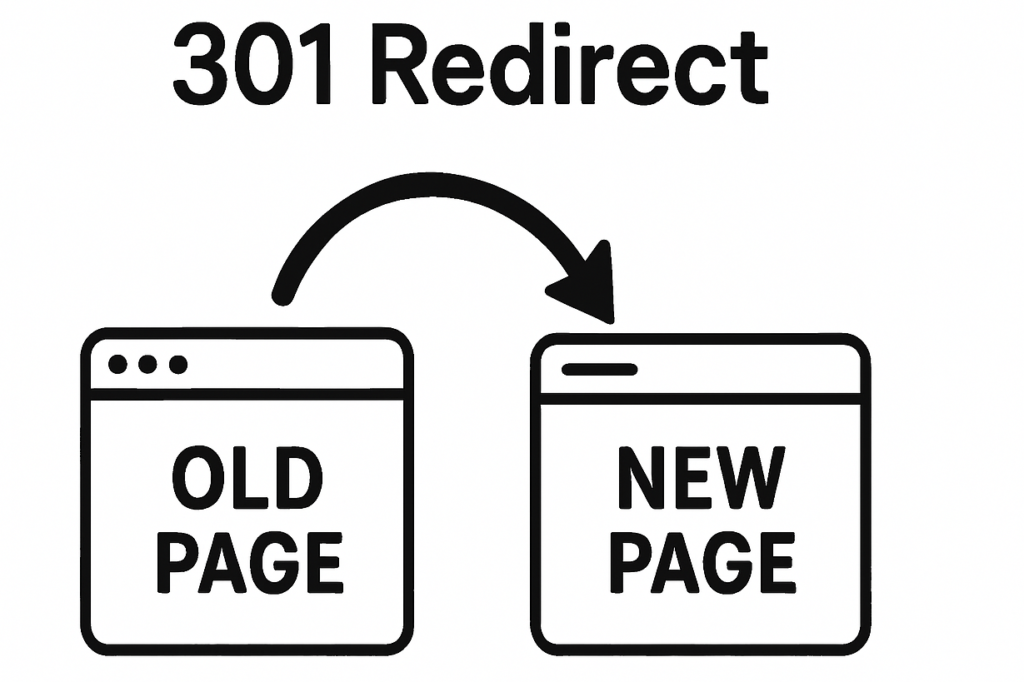
Take these steps to set it up:
- Modify the .htaccess file for Apache;
- Use a Redirection plugin in WordPress;
- Add a rewrite rule in the parameters file for NGINX.
Then, test the redirect by visiting the old link to guarantee it correctly forwards to the new alternative.
Check for Broken Links
As you already know, broken links might cause a “Not Found (404)” error. You can use diverse online tools to examine them, like
- Screaming Frog;
- Semrush;
- Ahrefs, etc.
After identifying these links, you have to remove or update them. Also, if external sites link to your deleted pages, contact the administrator to update them.
Examine Your DNS Settings
The DNS changes may take some time to propagate when you switch web hosts or your domain settings. The propagation process can take up to 24-48 hours, and your visitors may face 404 errors.
Contact your hosting service if DNS problems persist.
Step 3: Validate Fixes in Google Search Console
You made all the changes, and now you need to return to the “Pages” report in Google Search Console.
Click on any settled issues and pick the “Validate Fix” button. It will inform Google that you handled the errors.
Googlebot will then re-run the crawl to verify the adjustments. This confirmation process guarantees that it acknowledges your fixes and reflects them in search results.
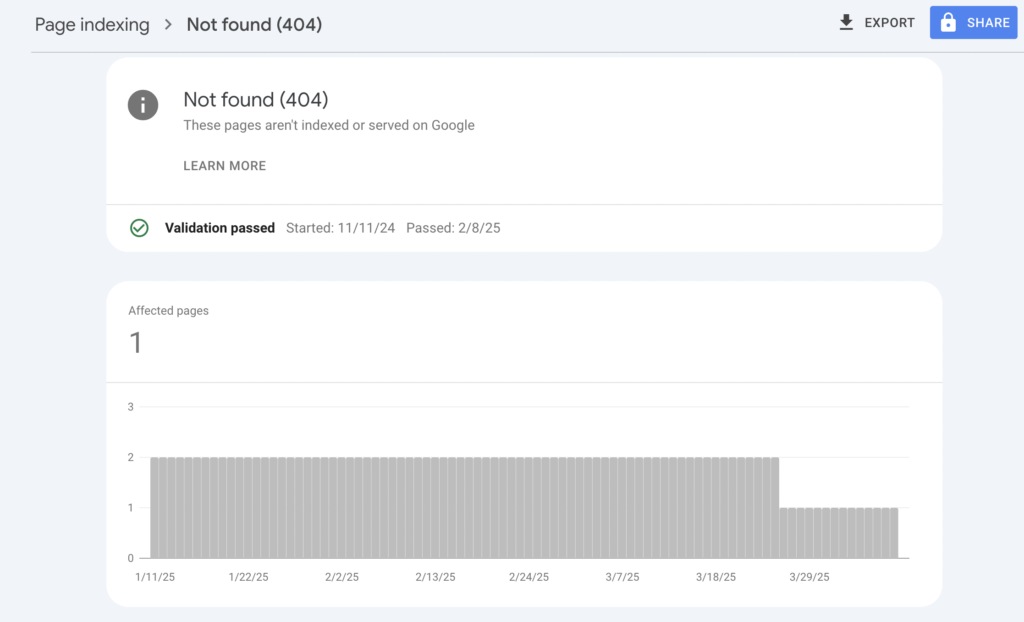
Step 4: Monitor Future 404 Errors
We suggest you regularly inspect your site to avoid possible cases of “Not Found (404)” errors.
Set up Google Analytics event tracking to monitor when users experience 404 pages. Also, you might use plugins for automatic broken link detection to simplify maintenance efforts.
Key Takeaways on Fixing the “Not Found (404)” Error
- The “Not Found (404)” error is a common issue. It’s not that big of a deal if you don’t face these errors too often;
- The main causes for this error are dead links, incorrect URLs, no redirects, etc.
- To resolve these problems:
- Evaluate the affected pages;
- Set up proper redirects;
- Remove broken links;
- Update your site;
- Validate fixes in Google Search Console.
If you encounter other errors, refer to our Google Search Console guidelines to resolve them.


