Latest update: April 24, 2025
The “Soft 404” error is a common problem for many websites. Googlebot gets confused with your pages and throws out this alert in Google Search Console.
These errors are odd in a way and it’s not always obvious what causes them. Yet, they are dangerous, as they might lead to indexing issues for you.
Keep reading and learn how to resolve them!
What is a “Soft 404” Error?
A “Soft 404” error is a tricky response from a web server. It appears in Google Search Console when your page seems to be missing. Yet, it still returns a 200 HTTP status code rather than the appropriate 404 code.
A valid 404 error response notifies users and search engines that the page is missing. Soft 404 gives the impression that the page is functional.
These errors usually occur because of improper server configurations or CMS settings.
Main causes of “Soft 404” Error
Here are the main causes you should know about.
Custom Error Pages Returning 200 Status Codes
Your site might have custom-designed error pages. They display a “Page Not Found” message while incorrectly returning a 200 status code.
This misconfiguration misleads search engines. They start treating the page as valid instead of nonexistent.
Thin or Empty Pages
Pages that exist but have very little content may also be classified as Soft 404s. This includes
- Empty category pages;
- Outdated product pages with no stock info;
- Placeholder pages, etc.
Search engines interpret them as non-useful and may flag them as errors.
Unrelated Redirects
Search engines treat the redirect as a “Soft 404” error when you route a missing page to a generic or unrelated destination.
This issue usually appears when site owners try to keep users on the website instead of displaying a broken link message.
Dynamically Generated URLs
Some sites generate URLs dynamically. It leads to cases where missing or inaccurate URLs still display valid-looking pages without content. Search engines usually flag these links as Soft 404s.
Inaccurate CMS Settings
Certain CMS solutions or server configurations may default to returning a 200 OK status even when content is missing. They can’t handle deleted or removed pages properly. So, you get “Soft 404” errors instead of standard 404 or 410 responses.
The SEO Impact of “Soft 404” Errors
You already understand why a “Soft 404” error appears in GSC. Your page returns a 200 status code even though the content is missing or irrelevant.
You’re probably wondering – “Does it even matter?”
This problem might seem minor, but it has some negative effects.
Poor User Experience
Users often land on pages that are empty or irrelevant when they experience “Soft 404” errors. It leads to much higher bounce rates and a drop in engagement because of their frustration.
Bad UX discourages people from revisiting your site. They might even share their opinion online, which damages your credibility and reputation.
Wasted Crawl Budget
Search engines have a certain crawl budget for each website. This budget determines how many pages they will index in a given timeframe.
“Soft 404” errors consume this budget unnecessarily. As a result, your important pages don’t get crawled and indexed. It leads to delays in the discovery of new content.
Weaker SEO Performance
These errors weaken your site’s SEO strength. Search engines devalue the authority of your site and lower it in rankings. As a result, your visibility becomes worse, and you won’t get much organic traffic.
Plus, frequent Soft 404s stop the crawling of certain sections of your site. So, any new materials that you post won’t rank either.
Inaccurate Website Metrics
Web analytics tools may misinterpret soft 404 pages as functional. They will give you misleading data on
- Page visits;
- Time on site;
- Engagement, etc.
You will find it hard to analyze user behavior patterns and make optimization decisions.
Step-by-Step Guide to Fixing the “Soft 404” Error
Managing “Soft 404” errors is essential for maintaining your site optimized and “healthy”. By leaving them unresolved, you might experience SEO problems and negative feedback from users.
We gathered the main steps you need to follow to address these errors.
Step1: Find the “Soft 404” Error
You need to determine which pages on your site were affected by Soft 404s before you can fix them. You may approach it in different ways.
First, go to your Google Search Console and open the “Pages” report. You will see the section “Why pages aren’t indexed“. It displays all the errors that limit your site.
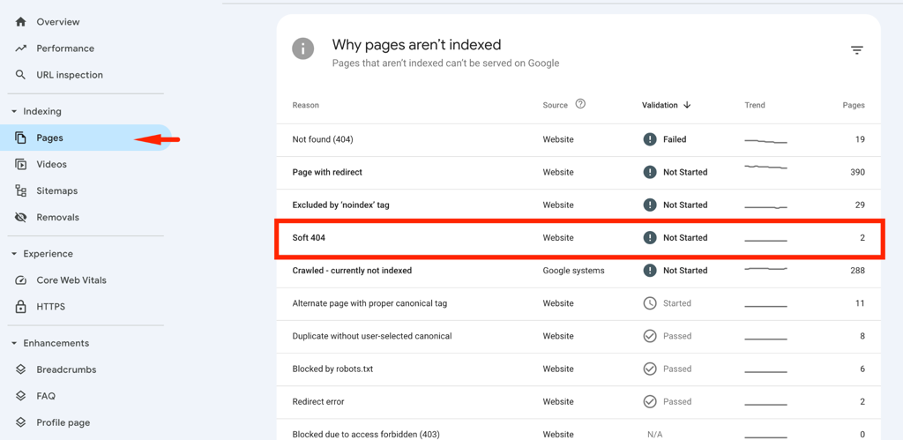
Also, you can use diverse crawling tools to identify this problem. Some popular alternatives are
- Screaming Frog,
- Sitebulb,
- Ahrefs.
They allow you to crawl your site and detect pages that return a 200 status code despite the error messages.
Another helpful tool is Google Analytics. You can use it to evaluate user behavior metrics, like high bounce rates and very short time-on-page. These metrics usually indicate that your page lacks useful content.
Step 2: Confirm the Problem
You’ve identified potential pages with a “Soft 404” error. Now, it’s time to manually inspect them to verify the problem.
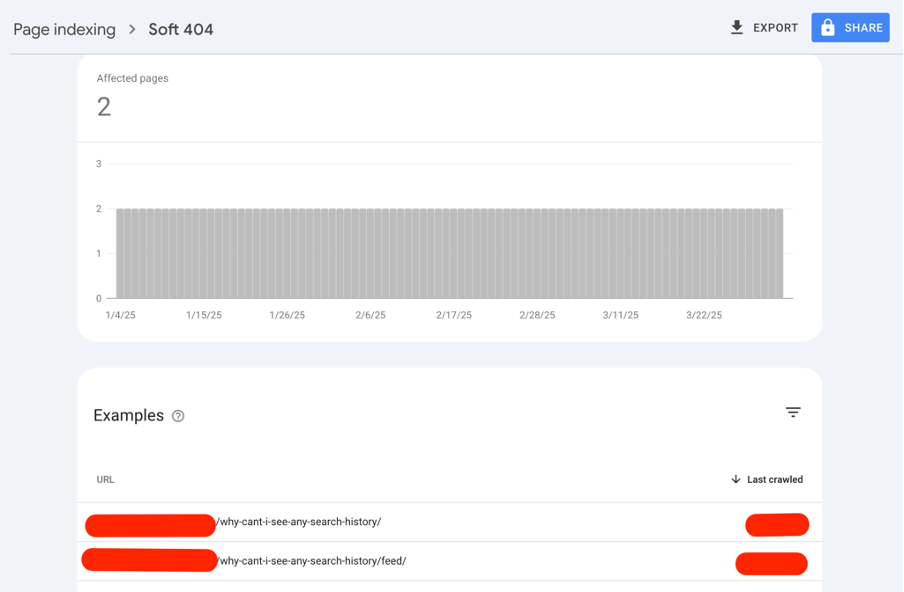
Certain signs might be apparent indicators of this issue.
Pages that don’t have meaningful content and simply state that the content is missing are a big red flag.
Another indicator is if your page appears blank or includes only a generic error message but still returns a 200 OK status code.
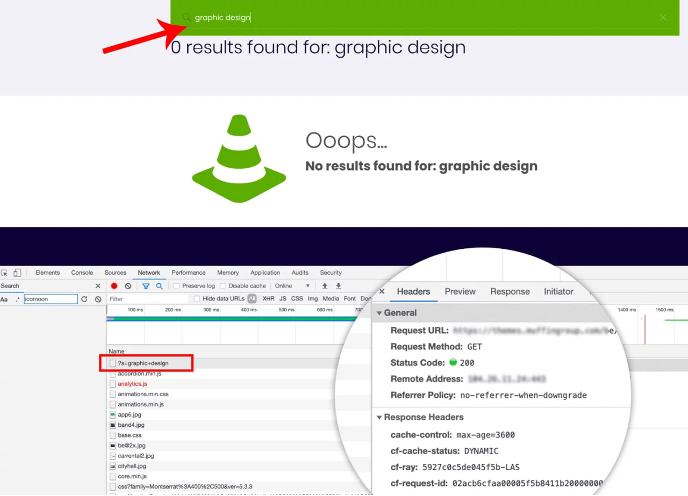
Also, you might experience a situation when your page is completely fine. However, it may be incorrectly classified as a Soft 404.
Verification will help you apply the best measures and avoid mistakenly modifying valuable pages.
Step 3: Pick the Right Fix
You need to find the most appropriate solution after diagnosing and confirming the issue. The fix will depend on the nuances of the “Soft 404” error.
Here are some measures you can take.
Implement a 404 or 410 Status Code
Your page should return a 404 or 410 status code if it no longer exists.
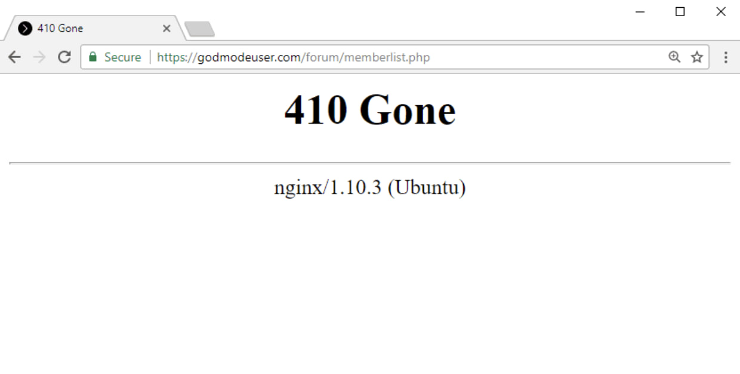
This status tells search engines that your page is unavailable. They won’t index it by knowing this information.
You can implement it by modifying the server configuration or manually updating the .htaccess file.
Improve the Content
Next, you can improve your site with new content. Make sure to add relevant and quality information that will benefit your visitors.
Confirm that metadata reflects your page’s purpose correctly. Also, don’t forget to update your materials with engaging images or multimedia.
Redirect to a Relevant Page
You can use a 301 redirect if your page is removed but you have a similar alternative. It will lead visitors and search engines to the correct content.
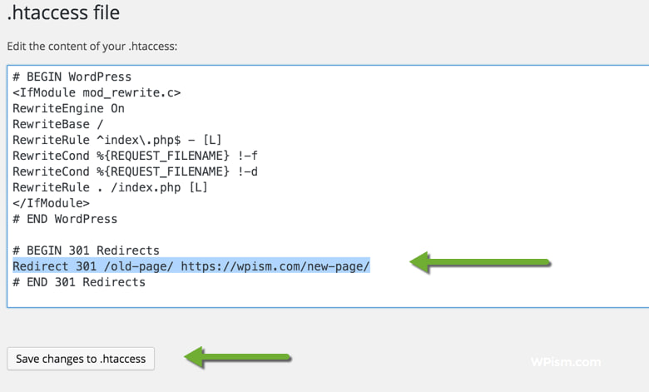
Here are some tips to follow during this activity:
- Don’t redirect to the homepage;
- Use a Permanent Redirect instead of 302 (Temporary);
- Avoid redirect chains.
Resolve Misconfigurations
As you already know, server misconfigurations or CMS mistakes sometimes lead to “Soft 404” error.
You have to check your CMS settings to confirm missing pages return the appropriate status code.
Also, verify that theme or plugin settings are not causing incorrect status codes if you’re using WordPress.
Remember, to review server logs to detect patterns of Soft 404 errors and adjust configurations accordingly.
Fix Internal Links
Broken internal links pointing to Soft 404 pages waste the crawl budget. To manage this problem, you have to
- Find broken links with a crawling tool;
- Update links to point to existing content;
- Remove dead links if no alternative content exists.
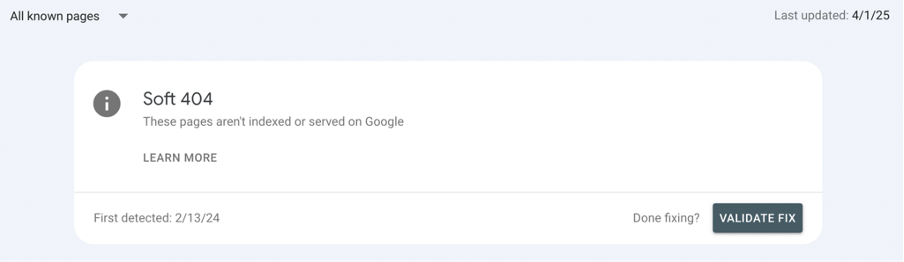
Step 4: Validate Page
The last step you should take is validation.
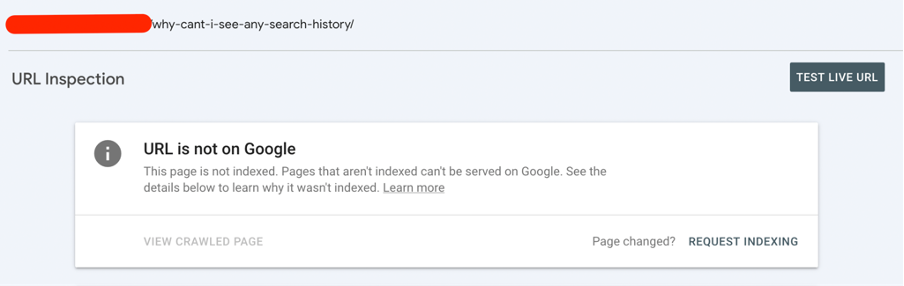
Visit your Google Search Console again and go to the “Pages” section. Click on the affected URL and press the “Validate fix” button.
Next, you can use the “Request indexing” option in the URL Inspection area.
Also, we recommend checking the Google Analytics reports from time to time. It will help you evaluate if users interact positively with the updated pages.
Key Takeaways on Fixing the “Soft 404” Error in GSC
Fixing the “Soft 404” error is essential for proper indexing and positive UX.
Common causes for this error are empty pages, unrelated redirects or incorrect CMS settings.
To fix this problem, improve your content, use the right status codes, and resolve any misconfigurations.
If you encounter other errors, refer to our Google Search Console guidelines to resolve them.


